Early life adversity (ELA)
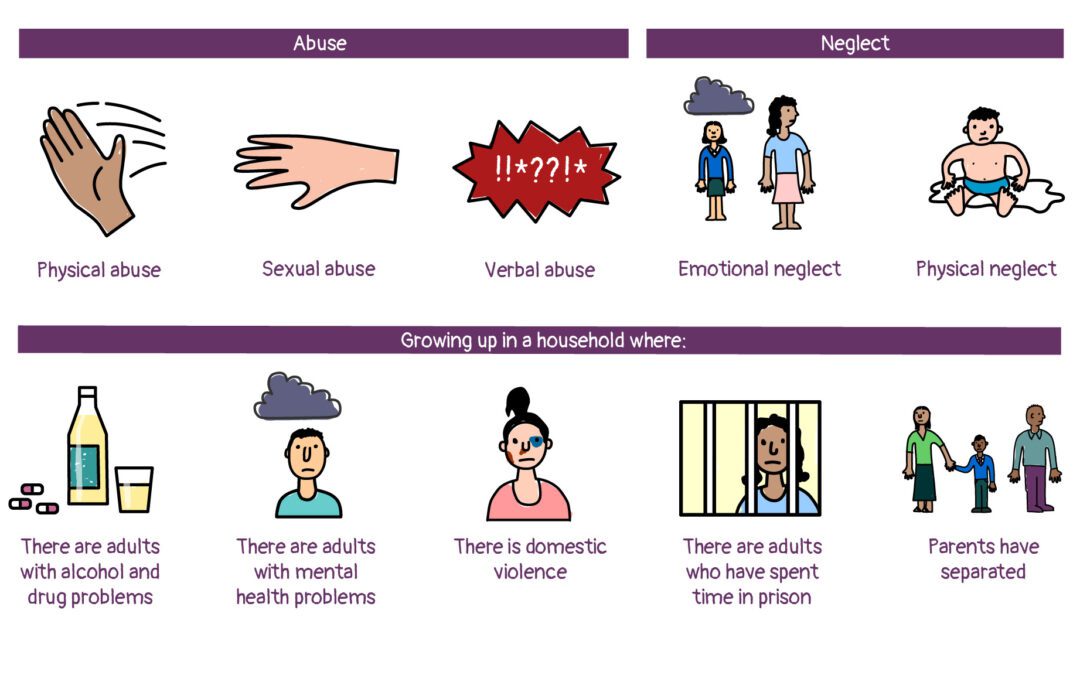
Exposure to environmental situations throughout childhood or adolescence that constitute a divergence from the usual environment and are likely to need considerable psychological, behavioural, or neurobiological adaptation by an average child is known as early life adversity (ELA) (Malave, van Dijk and Anacker, 2022). This definition of ELA encompasses a wide range of experiences, from long-term emotional or physical neglect to physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, as well as chronic material deprivation linked to poverty (Turecki et al., 2014). ELA exposure is frequent. Poor physical health outcomes in infancy and adolescence, as well as into adulthood, are linked to factors including childhood maltreatment and other types of familial dysfunction (Lopez et al., 2021). There was a correlation between the time of pubertal development and specific markers of childhood adversity, but the results were mixed (Murthy and Gould, 2020). Sexual abuse, father absence from the home, and family dysfunction were found to be significantly associated with ELA (Maccari et al., 2014).
Poor results for the children are linked to maternal psychological stress during pregnancy (Andersen, 2022). Numerous studies conducted on a diverse range of demographics and methodologies have confirmed the association between adverse prenatal experiences and altered development of critical bodily systems, reduced foetal growth, elevated risk of preterm delivery, and….
To get access to the complete article, please send an email at sales@thedocumentco.com

Recent Comments